Software Project
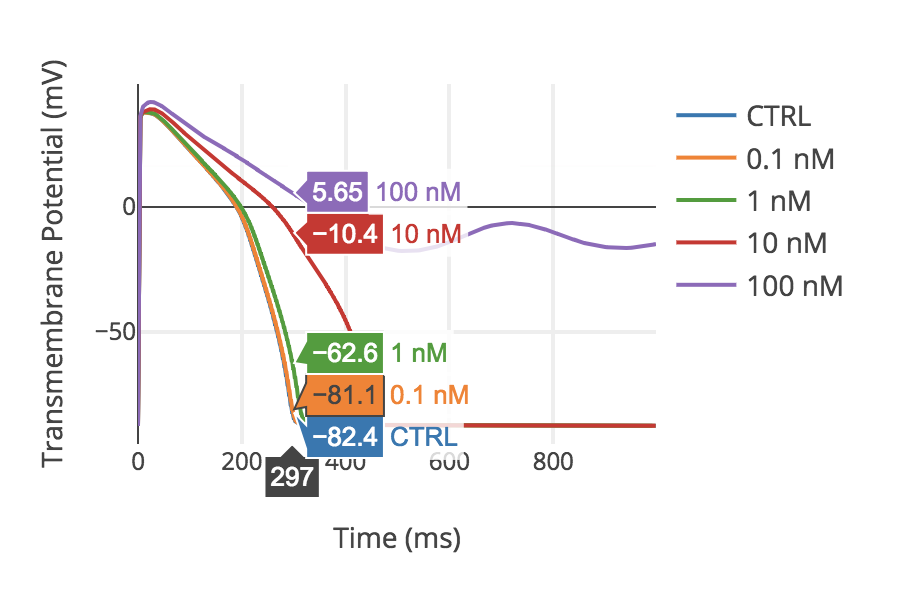
The Virtual Assay software provides a framework to run in silico drug trials in populations of human cardiac cell models for predictions of drug safety and efficacy. Virtual Assay starts with well-understood human cellular biology models and modulates the variables to generate a range, or population, of models, which will respond differently to the same inputs. These populations are then calibrated against experimental data, retaining only those models in Calibrated Model Populations range with experimental observations. Once calibrated, these populations can be used to analyse the effects of different pharmaceutical agents on cellular response at the population level.
Offered By
Use scenario
Clinical research, Clinical decision support, Non-clinical research.
HPC motivation
Generate large populations models for drug testing.
Relevant links
Related Articles
- Human in silico drug trials demonstrate higher accuracy than animal models in predicting clinical pro-arrhythmic cardiotoxicity. E. Passini, O. J. Britton, H.R. Lu, J. Rohrbacher, A.N. Hermans, D.J. Gallacher, R.J.H Greig, A. Bueno-Orovio, B. Rodriguez. Frontiers in Physiology. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00668. 8:668. 2017.
- Experimentally−calibrated population of models predicts and explains inter−subject variability in cardiac cellular electrophysiology. O. Britton‚ A. Bueno−Orovio‚ K. Van Ammel‚ HR. Lu‚ R. Towart‚ DJ. Gallacher and B. Rodriguez. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (23): E2098-E2105. doi:10.1073/pnas.1304382110. 2013.
 |
 |

